| printable version | torquemotor-teststand | ||||||||
Electrification of vehicle drives is coming up more and more. The battery is the most important object. Till today weight of the enery content is 10 times of that with gasoline. And the costs are a lot. Energy balance is only then ok if charging current is generated by regenerative means. All these developments are going on. If the battery is heavy then the vehicle itself must be eased, new material is being developped for that purpose. | |||||||||
| |||||||||
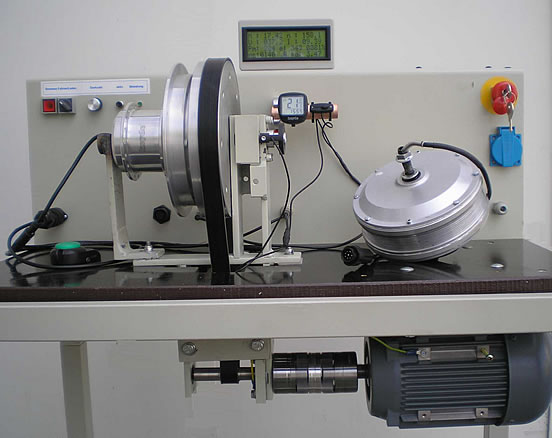
Build-up:
| |||||||||
Technical data of the teststand:
| |||||||||
The operational functions on the teststand:
| |||||||||
Experimental possibilities:
| |||||||||
| Discrete Measurement on in- and outputs of the controller Part of the cabinet can be opened from behind. Controller, charger, battery and all connectors are visible and accessable. With help of external measure instruments status, voltages and currents can be measured. | |||||||||
| |||||||||
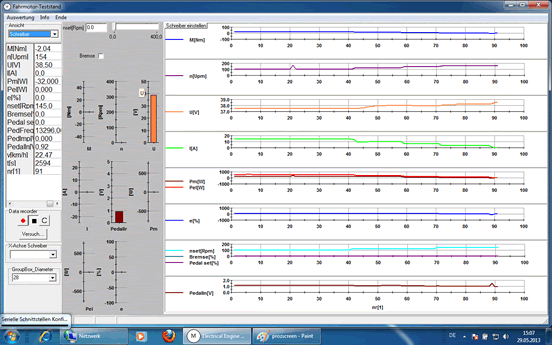
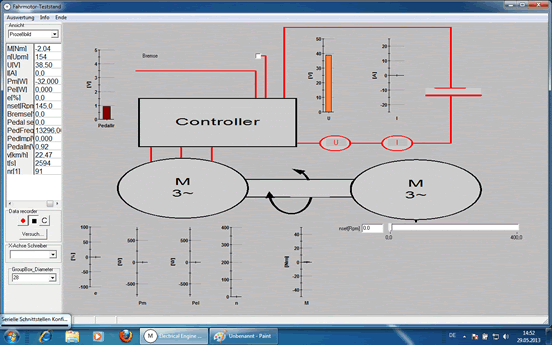
| TeLC software: Acquisition screen as process image or as plotter see below. Included are remote control and switching functions. | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
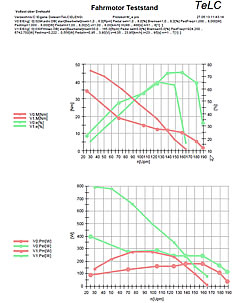
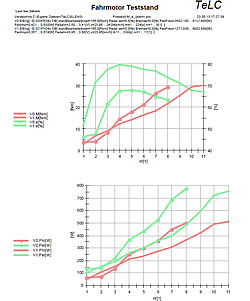
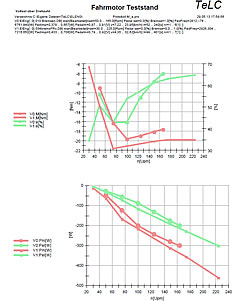
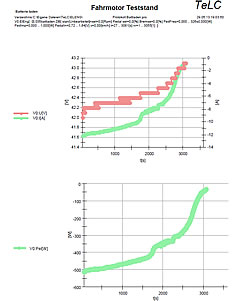
| Reports of some typical tests Multiple data files can be plotted with predefined graphs..Data were concentrated (edited) Tableform data export f.e. to Excell is provided | |||||||||
| |||||||||
Stichworte: Motortechnik Übungsstand, Leistungsprüfstand, Motorleistungsprüfstand, Ventilverstellung, Indizieren, Viertakt Motor Modell, Ottomotor Modell, Motorprüfstand Messtechnik, Motorprüfstand Datenerfassung, Verbrennungsprozess, Ventilsteuerung, Druckindizierung, Motorprüfstand, Glaszylinder-Motortechnik-Stand, Megatech, Glaszylinder, variable Ventilsteuerung, 4-Takt-Ottomotor, 4 Takt Motor, 4 Takt Otto Motor, gläserner Zylinder, transparenter Zylinder, Kurbeltrieb, Kolben, Ventile, Zündung, Verbrennung, verschiedene Kraftstoffe, Saugrohr-Einspritzung, Einspritzung, Einspritzmenge, Einspritzzeitpunkt, Einlass, Auslass, Ventilhub, Zeit-Öffnungs-Querschnitt, elektronische Zündung, Kennfeldzündung, Schließwinkel, geregelter Katalysator, Kurbelwellenstellung, Lambda-Sonde, Abgastemperatur, Drehmoment, Motorbetriebszustand, Zünden, Einspritzen, Kraftstoffmenge, Ventilsteuerzeiten, Frühzündung, Spätzündung, Überschneidung, Einlassventil, Auslassventil, Einlaßventil, Auslaßventil, Kennpunkt, Kennfeld, Indizieren, Zylinderinnendruck, Motordrehmoment, angesaugte Luftmenge, Expandieren, Auswerfen, Ansaugen, Verdichten, Warmlauf, Kaltstart, Indikatordiagramm, Vorzündung, gute Gemischbildung, Steuerverfahren, Laststeuerverfahren, Spätes Einlass Öffnen, Spätes Einlaß Öffnen, Spätes Einlass Schliessen, Spätes Einlass Schließen, Wandkondensation, Kraftstoffverbrauch, Kurbelwellenwinkel, Laufgrenze, fett, mager, stöchiometrisches Verhältnis, P/V-Diagramm, Drosselklappe, Gaswechselschleife, Vollast, Teillast, Volllast, Teilllast, Verlustminimierung, Vier-Takt-Motorbremse, Motorbremse, völlig variable Ventilsteuerung, variable Steuerzeiten, Lambda-1-Technik, Magerbetrieb, Leistungssteuerung, Valvetronic |
|||||||||
| ©TeLC Unna 2004 | |||||||||